What Is a Practicum? Definition, Benefits, and Examples
In many professional and academic programs, practical experience is just as important as theoretical knowledge. This is where a practicum plays a crucial role. If you’re a student, educator, or professional exploring hands-on learning models, understanding what a practicum is can help you make informed decisions about your education and career path.
This article explains the meaning of a practicum, how it works, its benefits, real-world examples, and the difference between a practicum and an internship.
What Is a Practicum?
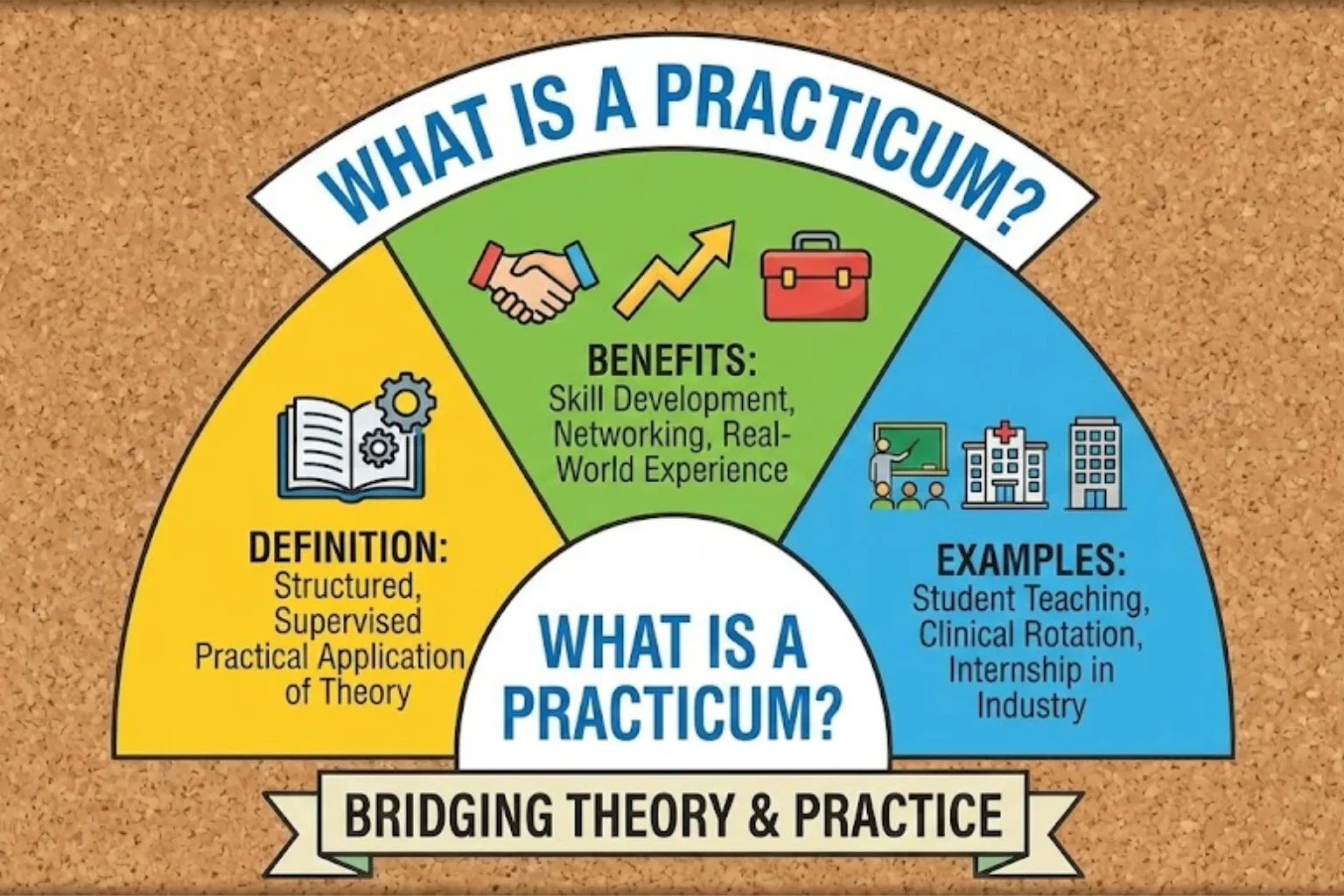
A practicum is a structured, supervised learning experience that allows students to apply theoretical knowledge in a real-world or simulated professional setting. It is usually a mandatory component of academic programs such as education, psychology, healthcare, counseling, and social work.
In simple terms, what is a practicum?
It is a guided training experience where learning objectives are closely tied to coursework and evaluated by academic supervisors.
Unlike informal work experience, a practicum follows strict academic guidelines, learning outcomes, and assessment criteria.
Purpose of a Practicum
The main goal of a practicum is to bridge the gap between classroom learning and professional practice. Practicum training ensures that students are not only knowledgeable but also competent in applying skills ethically and effectively.
Key purposes include:
Skill development under supervision
Real-world exposure within a controlled environment
Professional readiness
Confidence building
Ethical and practical application of theory
Practicum Training Explained
Practicum training is carefully designed and monitored by educational institutions. Students work in real or simulated environments while being supervised by qualified professionals.
Typical features of practicum training:
Clear learning objectives
Fixed number of required hours
Faculty supervision and evaluation
Reflection journals or reports
Performance assessments
Practicum training focuses more on learning and skill mastery than productivity or employment.
Institutions like Changa Institute emphasize structured practicum training that balances academic supervision with real-world skill development.
Practicum in Education
A practicum in education is one of the most common forms of practicum programs. It allows future teachers to gain classroom experience before becoming certified professionals.
Examples of practicum in education:
Observing classroom teaching
Lesson planning and delivery
Classroom management practice
Student assessment participation
Working under a mentor teacher
This type of practicum ensures educators are classroom-ready and understand real teaching dynamics beyond textbooks.
Examples of Practicum Programs
Here are some real-world practicum examples across different fields:
1. Psychology Practicum
Students conduct supervised counseling sessions, assessments, and observations in clinical settings.
2. Nursing Practicum
Nursing students practice patient care, medical procedures, and hospital protocols under supervision.
3. Education Practicum
Teaching students assist in classrooms, plan lessons, and manage student interactions.
4. Social Work Practicum
Students work with community organizations, handling case studies and client support under guidance.
These examples show how practicums are learning-focused rather than employment-focused.
What Is a Practicum Exam?
Many programs include a practicum exam as part of the assessment process. A what is a practicum exam question often comes up among students preparing for graduation.
A practicum exam may involve:
Demonstration of practical skills
Observation-based evaluation
Case study presentations
Teaching demonstrations
Clinical performance reviews
The purpose of a practicum exam is to assess competency, professionalism, and readiness to advance in the field.
Difference Between Practicum and Internship
Understanding the difference between practicum and internship is important because both provide hands-on experience, but their purpose and structures are different.
Practicum
Focuses on learning and skill development rather than employment
Supervised by academic instructors and field professionals
Usually short-term and part of a degree program
Unpaid in most cases
Almost always offers academic credit
A practicum is designed to help students apply classroom theory in a controlled and guided environment.
Internship
Focuses on gaining real-world work experience
Supervised mainly by a workplace or company supervisor
Typically longer in duration than a practicum
May be paid or unpaid, depending on the organization
Academic credit may or may not be provided
Internships are more job-oriented and help students prepare for full-time employment.
Practicum vs Internship: Key Takeaway
In a practicum vs internship comparison, a practicum emphasizes structured learning and supervision, while an internship emphasizes workplace exposure and professional experience. Choosing between the two depends on academic requirements and career goals.
Practicum vs Internship: Which Is Better?
Neither option is universally better — it depends on your goals.
Choose a practicum if:
You are early in your academic program
You need supervised skill development
Your degree requires it
Choose an internship if:
You want workplace exposure
You are closer to graduation
You want to build employability
Understanding practicum vs internship helps students plan their educational journey more effectively.
Benefits of a Practicum
A practicum offers several academic and professional advantages:
1. Hands-On Learning
Students apply theory in real scenarios, strengthening their understanding.
2. Supervised Skill Development
Mistakes become learning opportunities under expert guidance.
3. Professional Confidence
Practical exposure reduces anxiety and builds competence.
4. Ethical Practice
Students learn professional standards and boundaries.
5. Career Readiness
Graduates enter the workforce better prepared.
Who Needs a Practicum?
A practicum is especially important for:
Education students
Psychology and counseling students
Healthcare professionals
Social workers
Therapists and clinicians
In these fields, competence cannot be developed solely through theory.
For learners who require structured, supervised experience, dedicated practicum programs can provide guided, real-world training.
Final Thoughts
A practicum is a vital educational experience that transforms theoretical knowledge into practical expertise. Understanding what a practicum is, how practicum training works, and the difference between a practicum and an internship allows students to make informed academic and career decisions.
Whether it’s a practicum in education, healthcare, or psychology, this hands-on learning model ensures that graduates are not only qualified on paper but also capable in practice.